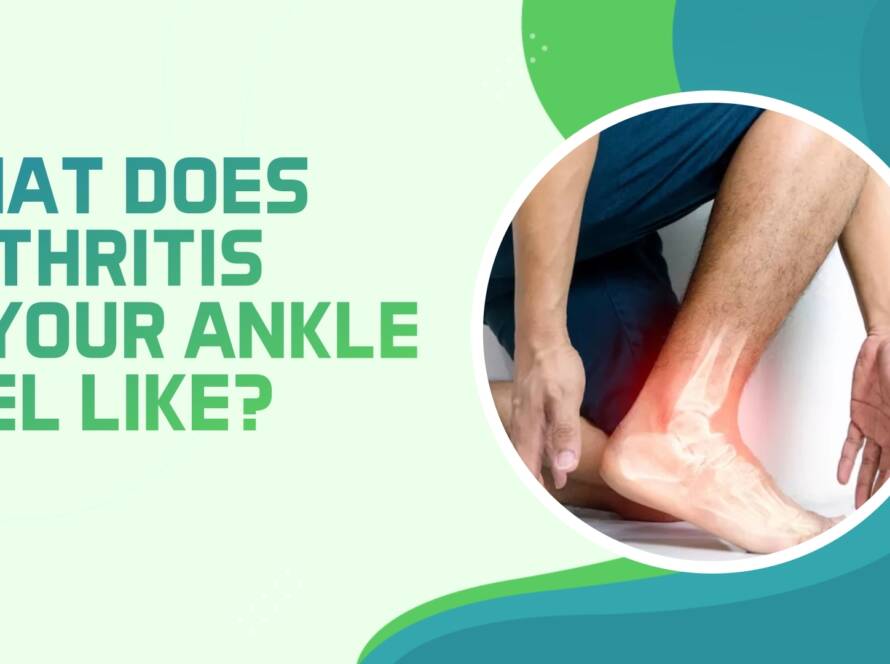
Do you or anyone in your family or close friend have a diabetic foot ulcer which is non-healing and difficult to manage? At Pro Foot, we can sympathize how painful and distressing such chronic wounds can be. Our distinguished podiatrists successfully managed many patients with ulcerectomies and advanced wound care.
Diabetes is one of the most prevalent diseases, and with it comes various complications, among them being issues related to the feet. Many of you might think that a small cut or blister does not warrant medical attention. Without treatment, such apparently trivial injuries can lead to serious wounds. It will be useful to consider why debridement may be needed in order to ensure proper care for one’s feet.
What is Debridement?
Debridement is a medical process where dead or damaged tissue is removed from a wound. It is a technique in which dead tissue is removed to promote healthy tissue growth and speed up the healing process.
It’s important because it removes microorganisms from the wound area and even reduces the risk of getting an infection. It also helps to create a new layer of skin on the body.
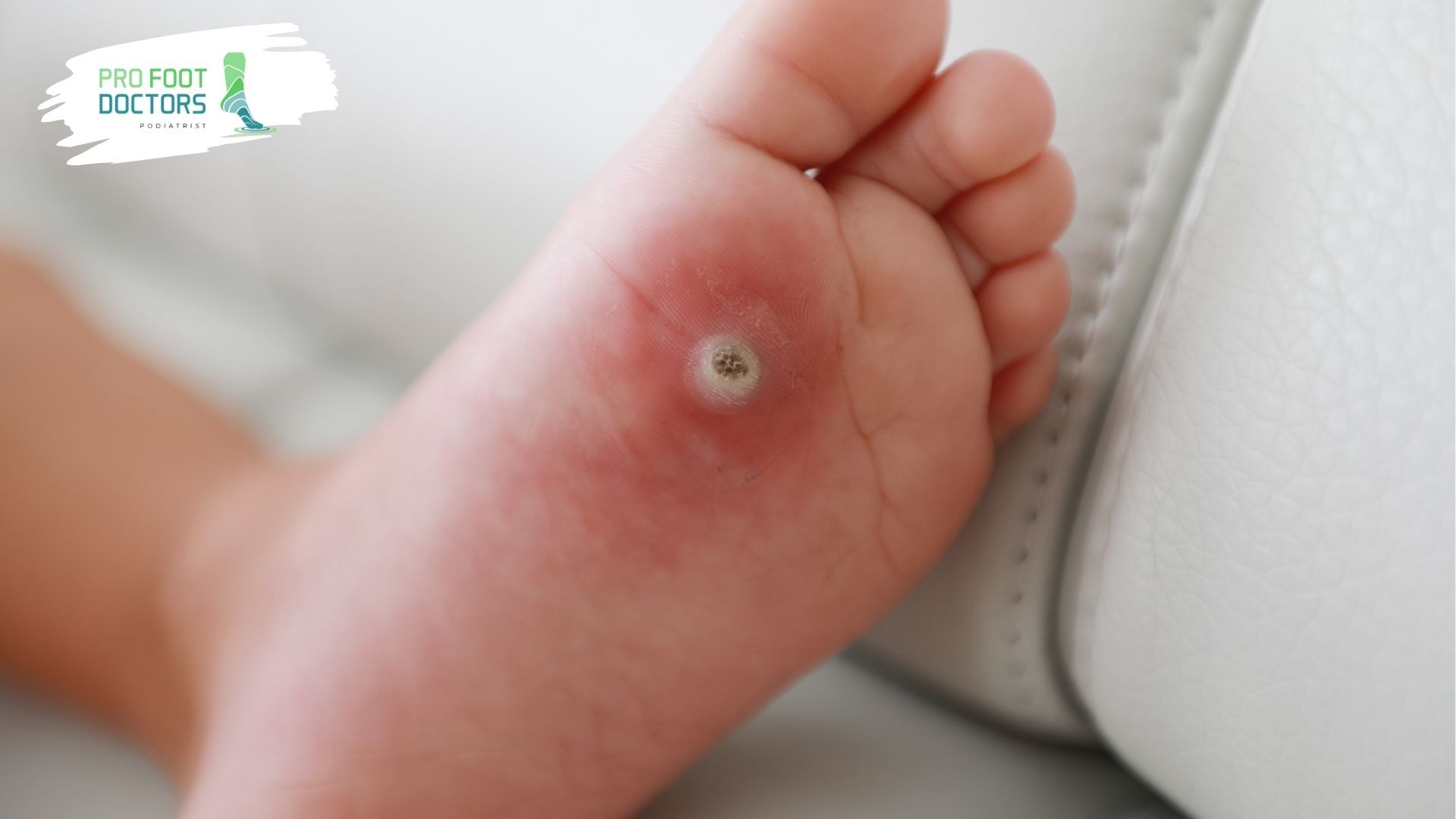
Why is Debridement Important for Diabetic Foot Wounds?
Diabetes is a systemic disease that is a challenge to wound healing. Poor blood supply and damage to the nerves further adds to the problem in the diabetic foot. Debridement is helpful in several aspects:
Elimination of Bacteria
Dead tissue is a source of bacteria infestation; this removal reduces the chances of infection.
Enhancing Wound Healing
A wound that is well debrided allows emergence of healthy tissue and, therefore, is more likely to resolve.
Enhancing Effect of Other Interventions
Other methods for example, dressings, antibiotics, or advanced wound care methods, are more effective where a wound has been appropriately debrided.
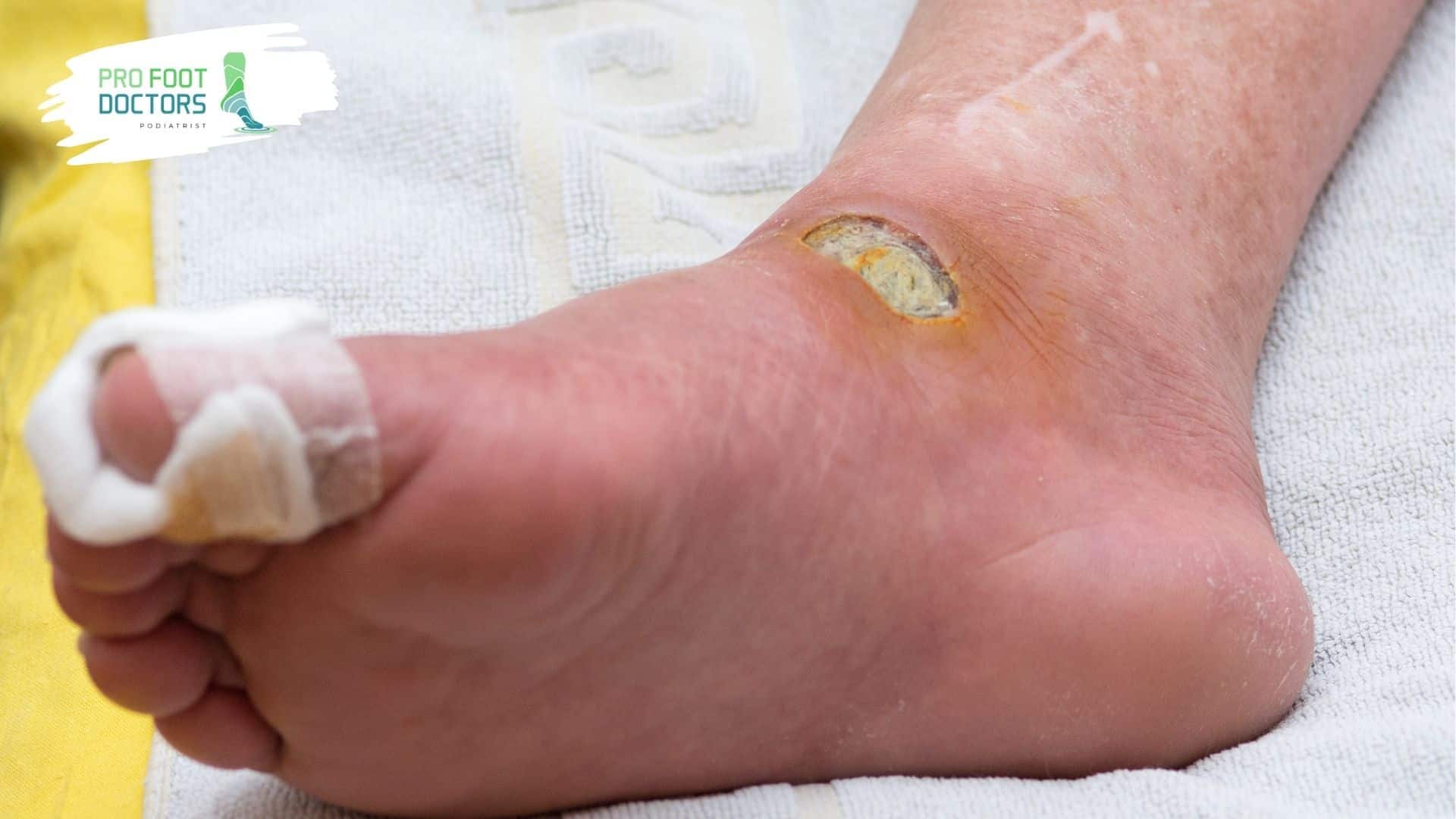
Types of Debridement
Debridement is clinically useful in many types, most of which present advantages and disadvantages. The most common include the following:
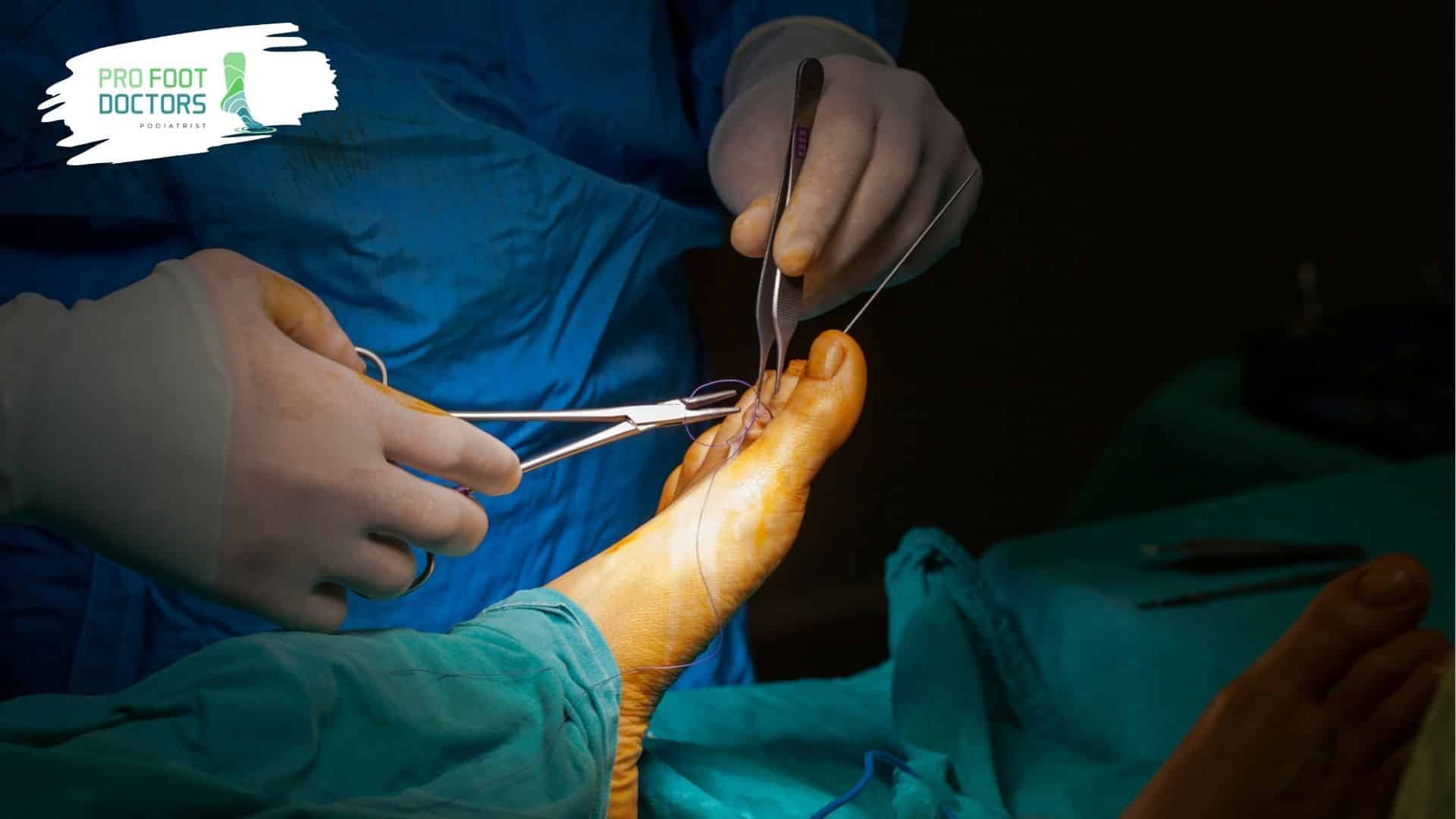
1. Surgical Debridement
Surgical debridement can be referred to as the most direct form. Here, instruments are used by a doctor to debride a wound.
These instruments are used in the same manner as a sculptor chipping away unnecessary sculpture pieces to expose the healthy ones. Moderately deep or infected wounds are usually treated through this method.
2. Mechanical Debridement
This method uses physical force to remove debris and dead tissue. A common technique is the wet-to-dry dressing, where a moist dressing is applied and allowed to dry.
When removed, it pulls away dead tissue with it—similar to using a lint roller. For wounds with moderate debris where less invasive methods are still effective.
3. Enzymatic Debridement
This method uses special ointments with enzymes that break down dead tissue. It’s like using a cleaning solution that dissolves dirt instead of scrubbing. For patients who cannot tolerate more aggressive methods.
4. Autolytic Debridement
This technique utilizes self-debridement’s own natural softening enzymes to promote the shedding of necrotic tissues. There are moist wound dressings which encourage the autolytic debridement of the wound.
Self-debridement is utilized for small and moderate-level wounds or the wounds of patients that can be treated conservatively.
5. Biological Debridement
The method also known as maggot therapy, utilizes solely biosurgical maggots as they feed on dead tissue, preserving healthy tissues.
Choosing the Right Method
The choice of debridement method depends on several factors:
Wound Size and Severity
Larger, deeper wounds may need surgical intervention, while smaller wounds might heal with autolytic or enzymatic methods.
Patient’s Overall Health
A patient’s pain tolerance, mobility, and underlying conditions influence the choice.
Availability of Resources
Certain procedures, such as maggot therapy or sophisticated enzymatic therapies, may not be available everywhere.
What Happens After Debridement?
Effective debridement has a substantial impact on wound healing results. When performed correctly, it:
1. Reduces Bacterial Load
Removing dead tissue minimizes bacterial breeding grounds, lowering the risk of infections. This creates an environment where healing can progress naturally.
2. Aids the Development of New Tissue
Wounds that are clean and well-perfused will tend to develop granulation tissue which is healing. This granulation tissue is pink and bumpy and this shows active healing.
3. Enhances the Effectiveness of Treatment
Debridement followed by other treatments like application of topical medications or dressings is more effective.
Risks and Complications
While debridement is generally safe and beneficial, it does carry some risks:
Bleeding
Especially when performed in patients with some blood dyscrasia (clotting disorders) or those that are anticoagulated.
Pain
In some techniques, pain such as mechanical and surgical debridement, may be experienced. Pain control is necessary.
Infection
Although this risk is diminished with proper technique it is always a factor that is present.
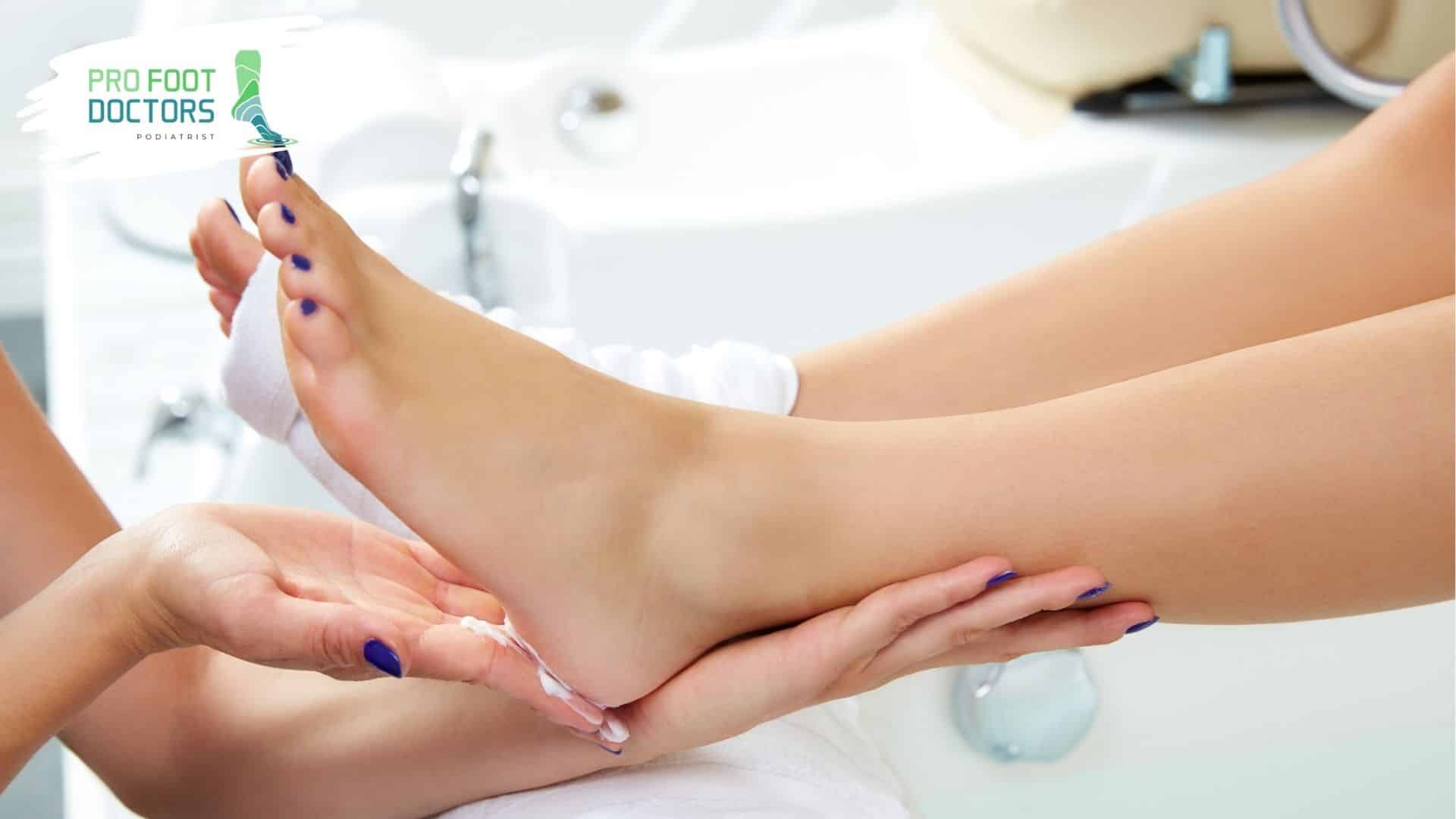

The Pro Foot Difference: Advanced Wound Care Solutions
Pro Foot goes beyond wound care. We offer more than wound care because we tackle the causes of the problem. We have a high-tech facility that allows us to implement several approaches – Professional Debridement Services, Surgical Debridement, Painless Mechanical Cleaning, and Enzyme Treatments.
We have treated thousands of diabetic foot wounds at our center and the results are impressive. We have also partnered with the emerging trends in wound care technologies to make sure you get the most effective treatment methods.
The longer you wait, the more complicated treatment becomes. Schedule your consultation today and take the first step toward healthy feet.
Conclusion
Debridement is an important stage in the process of treating diabetic foot lesions. By eliminating dead tissue, you lower the chance of infection, enhance healing, and make other therapies more successful. The appropriate approach, whether surgical, mechanical, enzymatic, autolytic, or biological, is determined by the condition of the wound and the demands of the patient.
By understanding the importance of debridement and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can take an active role in their recovery. Advances in technology and ongoing research promise even better options in the future. For more information on diabetic foot care, visit ProFootDoctors.com.
With proper care and attention, healing is achievable, improving both quality of life and overall well-being for those managing diabetic foot wounds.