The most prevalent cause of high ankle sprains is contact sports including basketball, hockey, rugby, and football. Because they occur in the ligaments over the ankle (over the ankle joint), these injuries are far more severe and challenging to diagnose than a typical ankle sprain, which is produced in the same place.
Being able to identify and treat high ankle sprains can be extremely beneficial for athletes, coaches, and sports fans.
What Is a High Ankle Sprain?
The syndesmotic ligaments (ligaments between the tibia and fibula) are stretched or torn due to overuse in rotational forces and are called a high ankle sprain. A more common type of this injury occurs during contact sports such as football, rugby, basketball, and soccer, where twisting, collisions, or falls are common.
A high ankle sprain is different from a standard ankle sprain, in which the foot rolls inward or outward, because this collapse frequently occurs in the combination of excessive dorsiflexion (when the toes are pushed upwards), and an excessive degree of rotation.
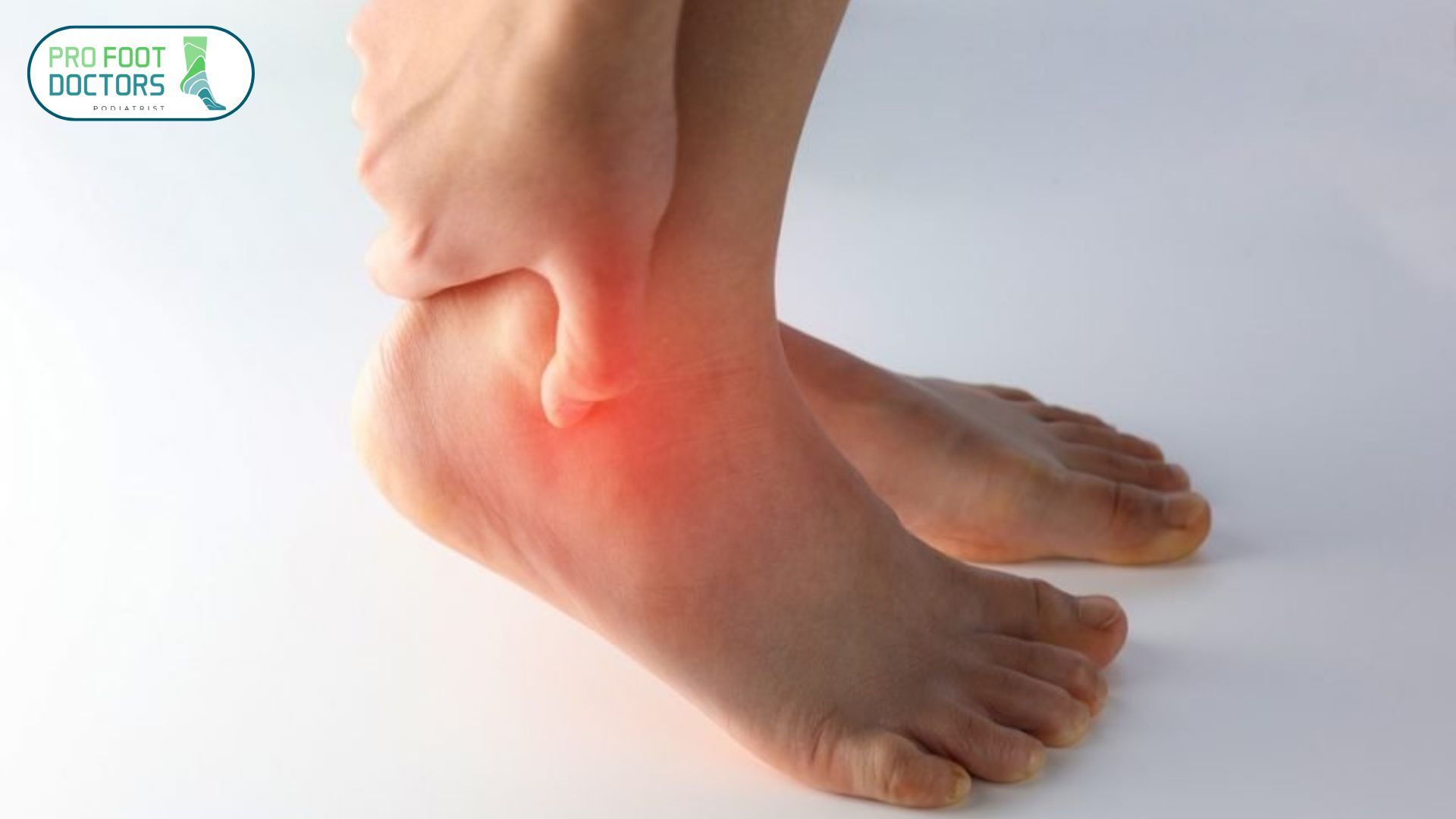
How to Identify a High Ankle Sprain?
Early diagnosis of high ankle sprains produces major implications for healing duration. Recognition of high ankle sprain becomes easier through identifying the following major signs and symptoms.
1. Pain Above the Ankle
High ankle sprains differ from standard ankle sprains because the affected area extends above the ankle bone toward the shin region.
2. Difficulty Bearing Weight
Generally, athletes suffering from a high ankle sprain can not walk on the injured leg or put pressure on the injured leg. Pushing off the foot or standing on tiptoes feels more painful.
3. Swelling and Bruising
While a high ankle sprain may not seem as obvious as bruising from a lower ankle sprain, bruising can still occur from the shinbone.
4. Tenderness Between the Tibia and Fibula
Sharp pain may occur if the tibia and fibula are pressed gently between the two bones, a sign of damage to the syndesmotic ligaments.
5. The Squeeze Test
Squeezing the lower calf together is a simple test for high ankle sprains. And if this action brings on pain above the ankle, it could be a syndesmotic injury.
Common Causes of High Ankle Sprains in Contact Sports
1. Twisting or Rotational Forces
When an athlete’s foot is planted while their body twists in the opposite direction, the syndesmotic ligaments can overstretch.
2. Direct Impact or Collision
Tackles, falls, or being stepped on can force the ankle into unnatural positions, causing a high ankle sprain.
3. Overuse or Repeated Stress
Athletes who perform repetitive jumping, cutting, or pivoting movements (such as basketball or soccer players) are at higher risk.
4. Wearing Improper Footwear
Shoes that don’t provide adequate ankle support can increase the risk of injuries, especially on uneven playing surfaces.
How to Treat a High Ankle Sprain?
1. Immediate First Aid
After a high ankle sprain, follow the R.I.C.E. protocol to minimize swelling and pain:
- Rest: Avoid putting weight on the injured leg. Using crutches may help.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage to reduce swelling, but don’t wrap it too tightly.
- Elevation: Keep the leg elevated above heart level to reduce inflammation.
2. Medical Evaluation
High ankle sprains can be unlike mild ankle sprains, and one may need to be assessed by a doctor. Ligament damage and fracture can be evaluated as to their severity with X-rays, MRIs, or stress tests.
3. Rehabilitation Exercises
A full recovery requires a structured rehabilitation plan once the pain settles.
Phase 1 – Mobility and Strengthening
The first step is to improve mobility. Ankle circles and alphabet tracing will help you to start with movement. Toe raises work to build the lower leg muscle. Resistance band exercises are gradually rebuilding the strength. These simple movements help the ankle avoid stiffness and prepare it for weight-bearing activities. Steady recovery is a function of consistency.
Phase 2 – Weight-Bearing and Balance Training
As mobility improves, balance becomes the main focus. Single-leg stands to improve strength and coordination. Mini squats activate supporting muscles. These exercises help the ankle to be safe to handle the tasks of daily life. Weight bearing is controlled which builds confidence against future injuries. Progression should be gradual and not have any setbacks.
Phase 3 – Sport-Specific Training
Athletes need targeted training. Jogging and lateral movements are reintroduced in the form of agility drills. The training works on controlled landing techniques. This phase steps up the strength, speed, and conditioning. A medical professional has to assess recovery before going back to full play. Through this mechanism, athletes can perform high-impact movements without facing any harmful consequences.
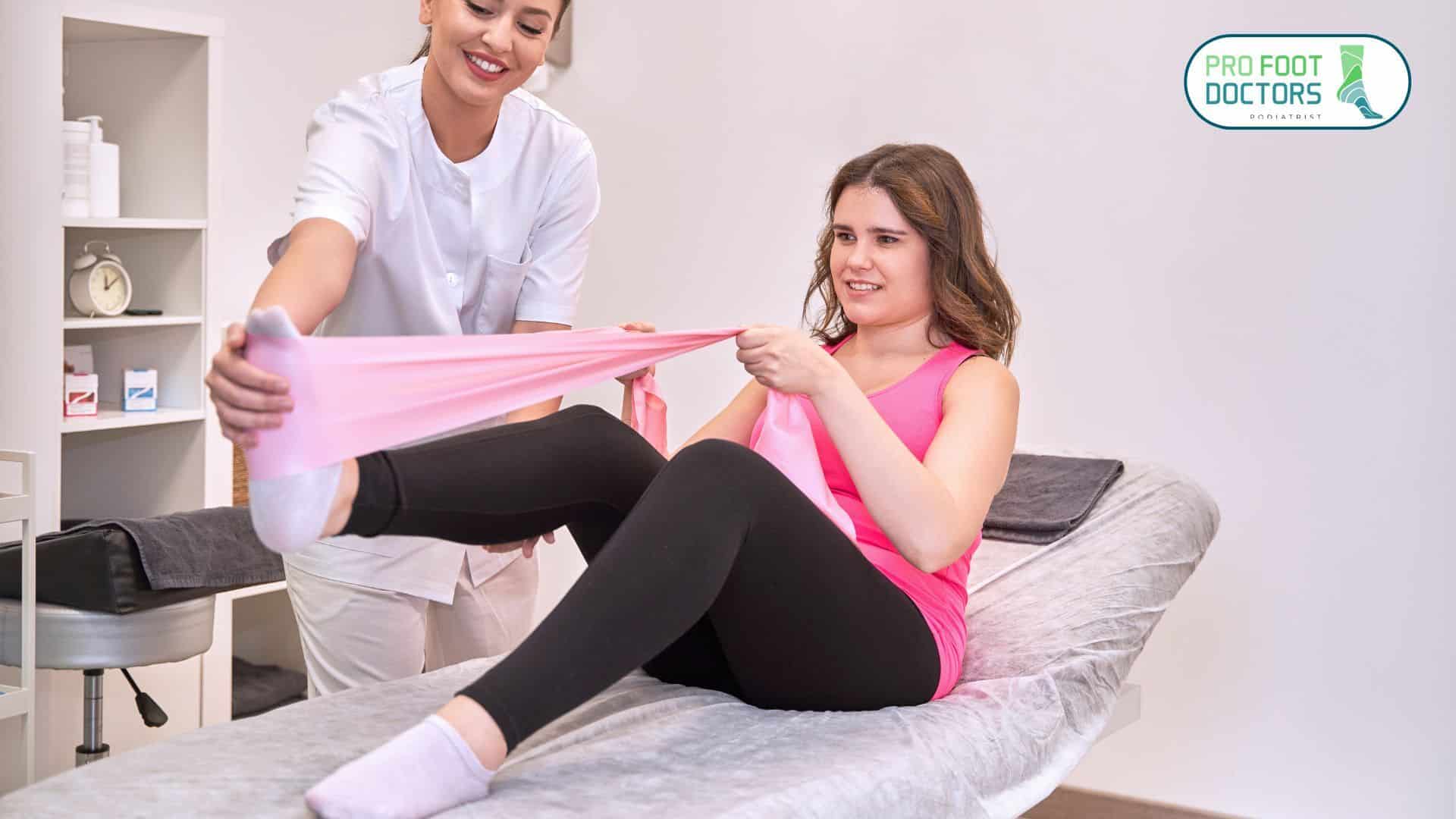

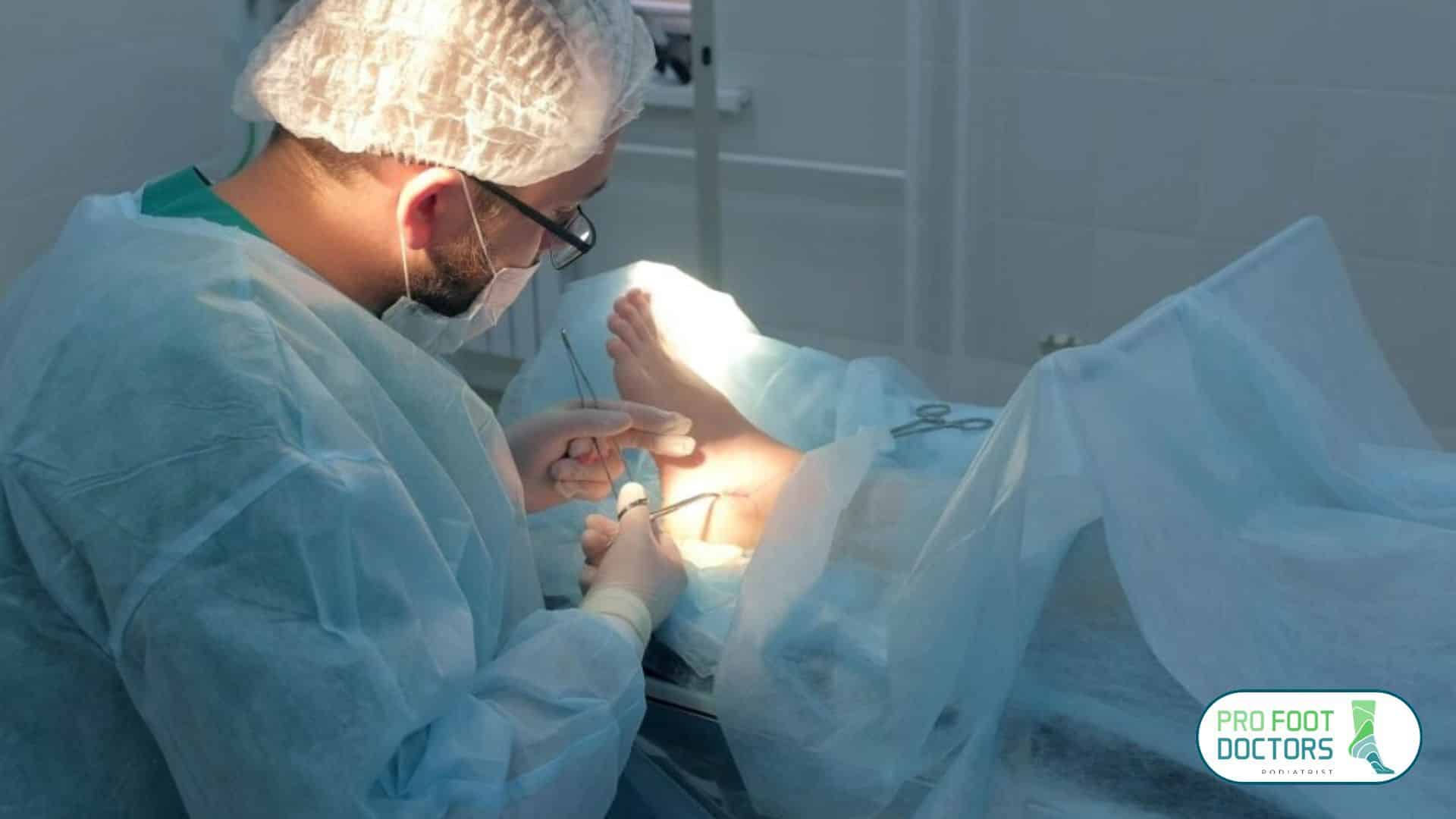
4. Surgical Intervention (For Severe Cases)
Ankle joint ligament damage or lack of stability will require surgery to stabilize the tibia and fibula through connections of screws or tightropes.
A study analyzed 100 professional football players with high ankle sprains. The research found that players who followed a structured rehabilitation program had a 30% faster recovery compared to those who didn’t.
This study highlights the importance of proper treatment and rehabilitation in ensuring a full recovery.
Preventing High Ankle Sprains in Contact Sports
1. Strengthening Exercises
The strength development of the lower legs along with the ankles helps minimize athletic injuries. Regular exercises, which include calf raises together with ankle mobility drills and plyometric workouts, enhance the stability level in athletes.
2. Proper Warm-up and Stretching
Dynamic warm-ups which consist of resistance bands, lunges, and ankle rolls, help athletes get ready for intense movement activities.
3. Wearing Supportive Footwear
Athletes should choose appropriate footwear for their sport since these shoes enable ankle support which also includes shock absorption as well as restraining unwanted foot movements.
4. Taping or Bracing the Ankle
Athletes need ankle tapes and supportive braces for stability enhancement which becomes especially important when participating in games and training activities.
5. Smart Play Techniques
Coaches and athletes should focus on proper movement techniques, including safe landing mechanics and controlled pivoting, to avoid awkward positions that increase injury risk.
When to See a Specialist?
If you suspect a high ankle sprain, especially if:
- You can’t bear weight on the injured ankle.
- There’s significant swelling, bruising, or deformity.
- The pain persists despite rest and care.
It’s time to consult a podiatrist. Early medical intervention helps stop the development of chronic ankle instability while reducing the possibility of long-term complications.
Trust Pro Foot Doctors to Receive Specialty Ankle Care Treatment From Experienced Medical Staff
The level of medical expertise you need for ankle injury treatment should be available to you. Specialized diagnosis and treatment exist at Pro Foot Doctors for ankle conditions that include both high ankle sprains and fractures of arthritis and continuing pain.
With advanced diagnostic instruments and individualized treatment approaches the experienced staff of our podiatrist specialists maintains high-quality results for sporting and athletic patients.
Pro Foot Doctors serve those who need diagnostic assessments in addition to rehabilitation recommendations and surgical consultations to improve their physical abilities.