Diabetes is a complicated health condition way beyond the control of blood sugar levels. One of the most dangerous diabetic issues is diabetic foot infections, which can turn a small cut into a serious health crisis.
For someone with diabetes, being aware of these infections is critical since early detection and comprehensive care can mean the difference between a successful course of treatment and significant consequences.
We at Pro Foot Doctors understand the importance of detecting diabetic foot infections early, treating them effectively, and maintaining them over time.
The Unique Nature of Diabetic Foot Infections
Diabetic foot infections are a complex medical condition that takes place owing to several physical problems. Diabetes affects blood flow—especially to the feet—decreasing the number of immune cells that can reach infected areas, which makes it very hard to fight infections.
Additionally, diabetic neuropathy can impair foot sensation, so patients may not notice blisters, wounds, or early infection symptoms for a long period. The body’s natural defenses against infections are weakened by high blood sugar levels.
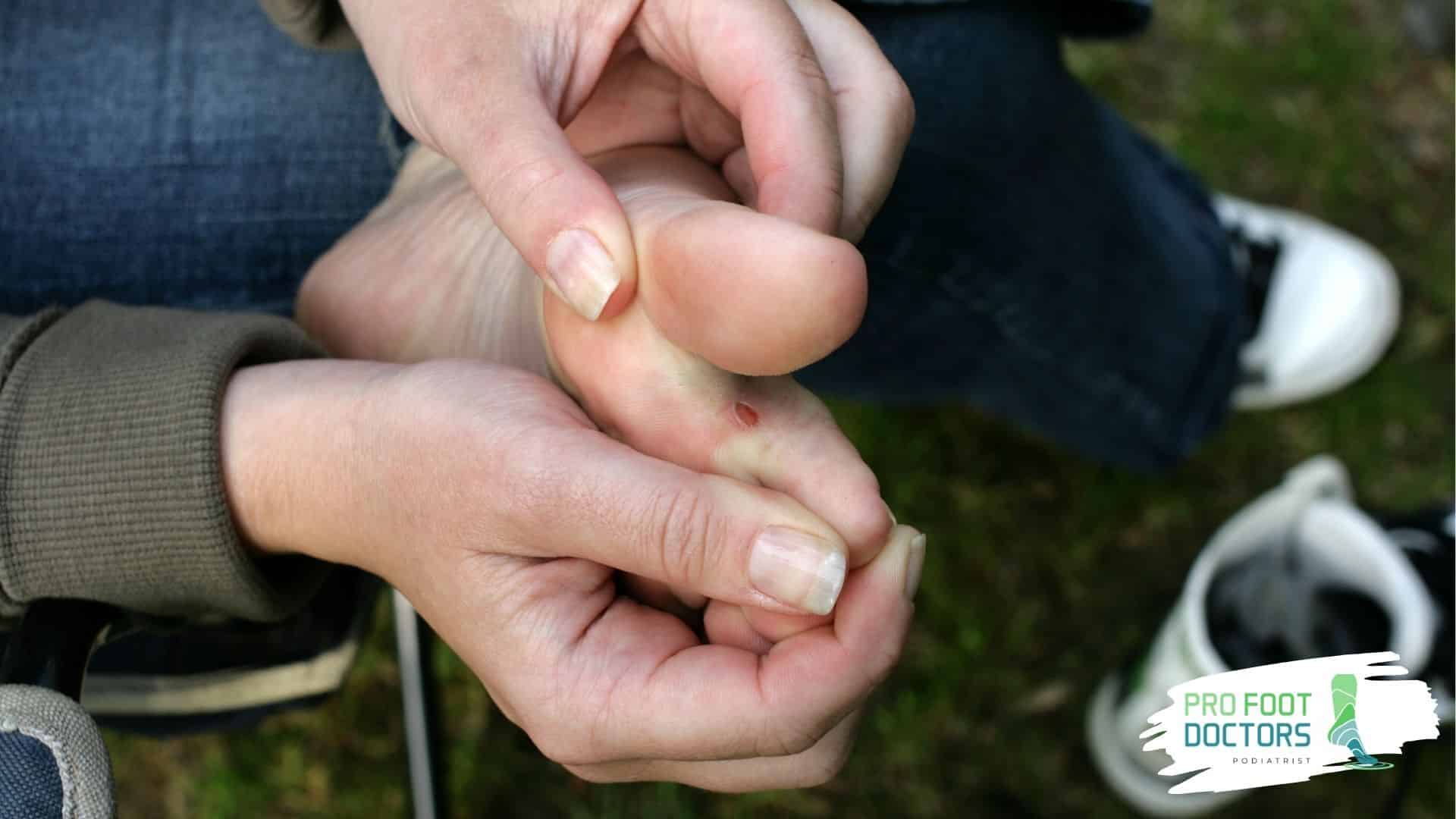
Categorizing Diabetic Foot Infections
Diabetic neuropathy is a big problem. The high levels of blood sugar can also hurt nerve endings over time, especially in the feet. This leads to the damage of nerves, known as peripheral neuropathy, whereby patients cannot feel their feet.
A small cut or blister that is not a big deal for someone without diabetes can become a serious risk for infection for a diabetic patient who cannot feel the injury at first.
Health-care professionals know that not all types of foot infections are the same. They classify diabetic foot infections by the seriousness of the infection and by depth.
Cellulitis affects only the top layers of the skin and is treated easily because medicine can easily reach it. Soft tissue infections go deeper than the superficial infections and can, if not treated, proceed to become dangerous thus, they need stronger methods of treatments.
The hardest and most complex type of infection is chronic osteomyelitis, which is an infection of the bone. It is very difficult to treat and usually requires surgery and a complicated treatment plan. Each of these infections requires a careful medical plan.
Early Detection
Early detection of diabetic foot infections is important. The patient should be alert and seek medical care immediately if they notice any of the following signs:
- Redness and swelling that lasts around a wound or part of the foot may mean an infection is starting.
- Unusual warmth in specific areas of the foot may indicate that inflammation is occurring.
- Discharge, especially if it looks like pus or smells bad, is a surefire red flag.
- Skin color changes, from being too pale to getting darker or even turning greenish, may indicate a problem with blood flow or an infection beginning.
Any persistent pain that does not follow the expected course of healing of a wound always warrants an investigation. Slow-healing wounds that fail to improve over a few days should be checked by a doctor.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies
The treatment of diabetic foot infection is multi-pronged:
1. Offloading: Reducing Mechanical Stress
Doctors have developed advanced techniques to shift the pressure away from infected parts of the foot. Total contact casting is considered the most effective method of treating plantar diabetic foot ulcers. The technique spreads out the pressure, thus allowing healing to be more within reach and increases the healing chances manifold.
2. Antimicrobial Therapy: Targeted Infection Control
The choice of the right antimicrobial treatment depends on the type and seriousness of the infection. For mild infections, doctors may give oral antibiotics that target bacteria on the skin. Medicines like cephalexin, dicloxacillin, and amoxicillin-clavulanate can work well against early stages of the infection.
More severe infections need more aggressive care. Inpatient hospitalization with IV antibiotics that cover a broad spectrum is necessary. Drugs like vancomycin, linezolid, and meropenem protect against multiple possible bacterial offenders.
3. Surgical Intervention: When Medication Isn’t Enough
Sometimes, surgery may be quite important. Surgical debridement involves the careful removal of infected pieces of bone to let the remaining tissue heal properly. Especially, long-standing cases of osteomyelitis need this surgery.
In extreme cases, amputation is the best medical option. While it is difficult to accept, the process prevents the infection from spreading and keeps the patient healthier.

The Critical Role of Glycemic Control
No discussion of the treatment for diabetic foot infections would be complete without mentioning glycemic control. Stable blood sugar levels are more than controlled diabetes; it forms part of the healing process
Good control of blood sugar helps wounds heal faster by keeping the body in a good state. It makes medicines work better, lowers the chance of getting infections again, and boosts the body’s immune system. Patients who work closely with their doctors to keep their blood sugar levels steady usually have much better results with infections.
Prevention and Proactive Care
The mainstays of diabetic foot infection prevention are based on a multipronged approach, including daily inspection of the feet by the patients themselves, good foot hygiene, proper well-fitting shoes, control of blood sugar levels, regular professional foot examination, and management of underlying health conditions.
Recent research showed that exercise could help with diabetic foot health. The regular physical activity helps decrease the number of foot ulcers, improve nerve function, make sensory performance better, and help in the even distribution of foot pressure.
Advanced Therapeutic Options
Contemporary and advanced wound healing modalities now being introduced into practice include allogeneic keratinocyte dressings and other cell products. Newer treatments are more likely to succeed in association with appropriate pressure-relieving techniques and meticulous medical care.
When To Seek Professional Help
Any chronic foot problems should be professionally medically checked. Non-healing wounds, infections that are spreading, unexplained pain, or obvious changes in the appearance of the foot all merit prompt consultation.
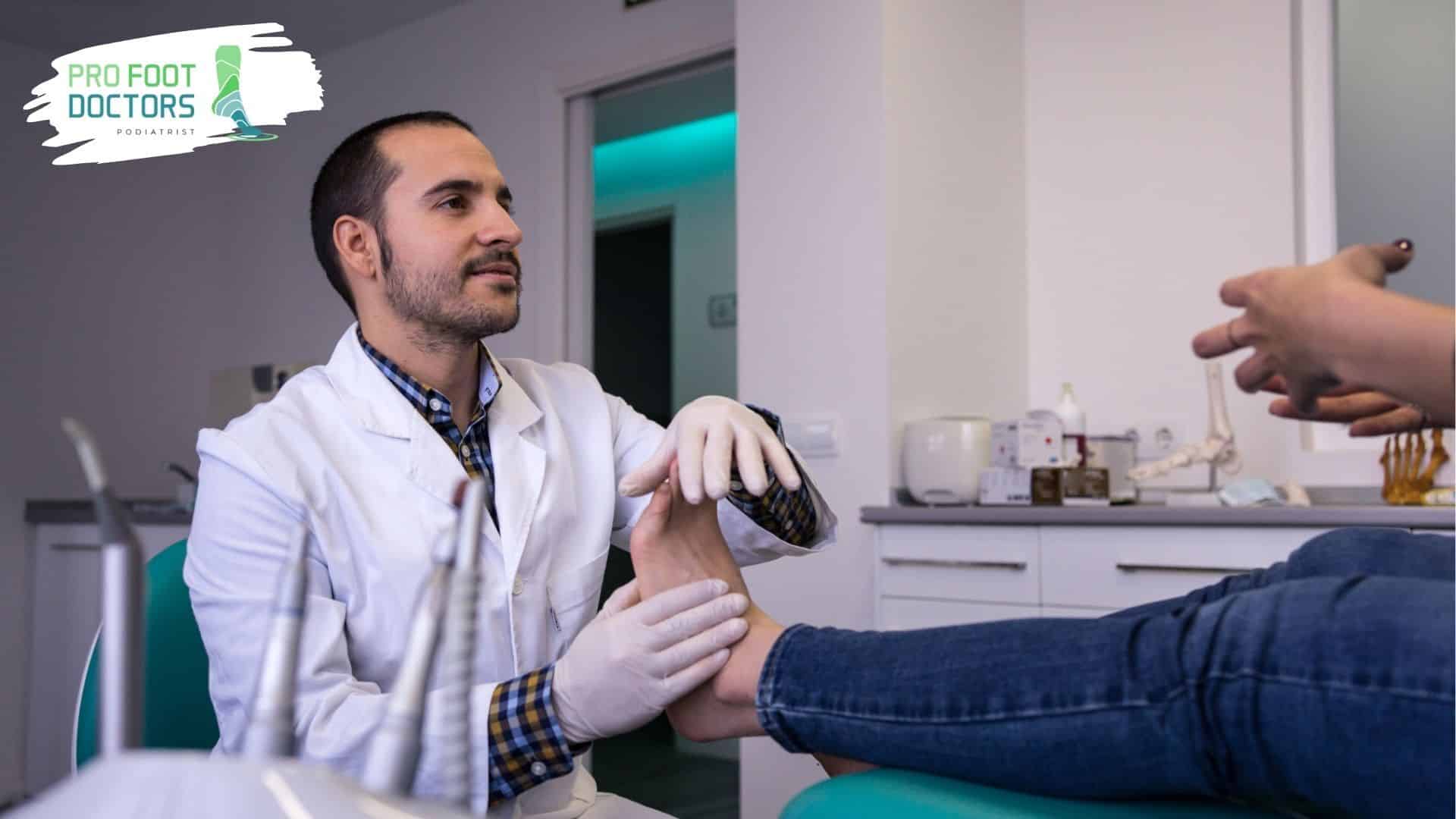

Conclusion: Empowering Patient Care
Diabetic foot infections are treatable even if they are a severe medical condition. In addition to obtaining routine care, patients who receive an early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent serious issues and maintain the health of their feet.
Our knowledgeable staff at Pro Foot Doctors specializes in diabetic foot care and provides individualized foot infection management and prevention techniques. We advise individuals to be proactive about the health of their feet and to consult a specialist whenever they have concerns.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is valuable but cannot take the place of professional medical advice. For personalized medical assistance, consult healthcare professionals at Pro Foot Doctors.